The following steps will describe in sequential order the process of IRB review from making the first decision of whether to apply for IRB approval to describing what to do after you have obtained approval.
Any Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) policies referenced throughout the following steps are based on federal regulatory requirements found at 45 CFR §46 (i.e., the Common Rule).
Step 1: Decide if you are conducting human subjects research
Step 2: Prepare your IRB application through NuRamp
Step 3: Begin the “Routing” process to submit the IRB form
Step 4: The Review Process
Step 5: IRB Approval (Criteria, Review Level and Category)
Step 6: Receive IRB Approval
Step 7: Organize the research documents
Step 8: Understand the responsibilities after approval
Step 1: Decide if you are conducting human subjects research
In order for a project to require oversight it must meet the regulatory definitions of research AND human subjects. Policy #3.001, “Investigational Activities Requiring IRB Review and Approval” defines activities that must be reviewed and approved by the IRB before the project begins (including recruitment and/or data/biospecimen access).
- Research is “a systematic investigation, including research development, testing, and evaluation, designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.”
- Human Subject is “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research, (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens, or (2) obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens service programs may include research activities.
Research utilizing secondary information and/or biospecimens that were previously collected for research or non-research purposes and will now be used in the proposed research study may require IRB approval. For projects that include the secondary analysis of data or biospecimens, investigators need to understand and be able to determine whether they have identifiable private information and/or biospecimens, which would require IRB review. Please refer to our Secondary Information and Biospecimens: Use in Research and IRB Applicability A-Z guidance and our Data Identifiability Definitions A-Z guidance for definitions related to data identifiability, which are both available here.
The decision of whether or not you are conducting human subjects research and whether or not an application for IRB review must be submitted can be made by the Principal Investigator. Policy #3.001, “Investigational Activities Requiring IRB Review and Approval” specifies that, “Any individual who is unsure whether or not a proposed activity constitutes research involving human subjects should contact the HRPP office for guidance.”
If you are unsure whether your project requires approval, you can:
- Submit a Determination Form via NuRamp for official review.
- Review the definitions above or the Human Subject Regulations Decision Charts available through the Office of Human Research Protections.
- The decision charts may not be used for exemption determinations, expedited review, or continuing review. Certain state laws and institutional policies, which may not be taken into account within the decision charts, could affect UNL IRB review categories and applicability.
- Contact Research Compliance, Integrity, and Security to discuss the project.
If your project requires IRB approval, please begin your application in NuRamp.
If your project does NOT require IRB approval, you are not required to submit an application for determination. However, please be aware, IRB approval may not be granted if the research has already started or been conducted and the determination of IRB applicability was made incorrectly by the investigator.
Step 2: Prepare your IRB application through NuRamp
(NuRamp URL: nuramp.nebraska.edu/)
All new projects are required to be submitted for review through UNL’s electronic research/grant administration system, NuRamp. All UNL faculty, staff, and students have access to NuRamp. Before beginning your application, the following items might be helpful:
-
- A guidance document has been created to assist investigators in answering questions on the NuRamp application for projects involving primary data collection.
- All forms specific to human subjects research are found in the Institutional Review Board module.
- All undergraduate, graduate, and post-doctoral trainees are required to submit their application with a faculty member as a Co-Investigator on the project. Usually, this person is the student’s advisor, committee chair, or mentor as a post-doctoral trainee.
- All project personnel must be listed on the Project page. Any member of the research team who interacts with a participant, obtains informed consent, has access to identifiable data, or analyzes collected data should be identified as a personnel member.
- All project personnel must have the appropriate human subjects research training.
- All project personnel must complete a project-specific conflict of interest disclosure.
- Administrative personnel can also be identified on the Project page. This could be anyone who needs to have access to the IRB protocol via NuRamp. This person may or may not be a project personnel member depending on their role.
- The IRB templates/forms webpage provides several Word documents that can be revised to be specific to your project including documents that are specific for use with Exempt research.
- The Guidance Topics (A – Z) webpage provides additional information and links to helpful resources on a variety of topics.
- All UNL Human Research Protections Program (HRPP) Policies and Procedures are available on our website.
- Multiple videos are available on the Video Resources page. These videos include specific topics related to research administration and NuRamp navigation.
NOTE: Take a moment to re-read the application before you officially submit for review. One of the most common delays experienced during the review process is due to inconsistent information. Investigators should feel free to use the PI Checklist for IRB Protocol Submission available on our Templates/Forms web page.
Step 3: Begin the “Routing” process to submit the IRB form
Once the form has been written and all applicable supporting documents have been uploaded, the form must be submitted through a “routing” process via NuRamp. The routing process triggers the IRB review process to officially begin. The routing process must be initiated via NuRamp by electronically signing the form and can be done so by either the Principal Investigator (PI), the Secondary Investigator (SI), or an administrative personnel member can notify the PI or SI. The routing process accomplishes multiple requirements such as:
- Certifications and attestations by the investigator(s) specifying sound research design has been used to achieve the aims of the study with the least amount of risk possible. Each investigator should review the protocol and ensure that all information included is clear, concise, and accurate.
- If applicable, the second person in the routing process submitting the form for official review has the option of “requesting revisions” prior to official submission. This is completed on the routing signature page and is one of two options available (i.e., approval vs. request revisions). If revisions are requested during the routing step, the applicable investigator will be notified via email.
- Only two investigators can be entered in the form itself. Typically, investigators who listed in the form are either the overall PI, including students, or are senior key personnel. If more than two individuals are identified as a Co-Investigator and they need access to the application via NuRamp, Co-Investigators should be added to the project personnel list and the administrative personnel list. See the video resource “Internal Project Personnel” for more details.
Step 4: The Review Process
Several steps take place during the review process of each project. These steps can vary depending on the review level of your project through the Exempt, Expedited, or Full Board review method. Generally speaking, each project will undergo a pre-review process, an official review process, and revisions completed, if required, by the research team. Once all regulatory requirements are met, the project will be approved.
- Pre-review step
Upon submission, the designated IRB Coordinator will review the form submitted to ensure clarity of information within the application, submission of all supporting documents, and confirmation of review level. - Official Review Step
Once the form meets the minimum criteria to be submitted for Exempt, Exempt with Limited Review, Expedited or Full Board review, the IRB coordinator will submit the form to the appropriate reviewer/Board. The IRB Coordinator also ensures the IRB reviewer and/or Board composition has the appropriate expertise based on background, training and familiarity with the research and/or procedures.- Exempt review is conducted by IRB Coordinator.
- Exempt with limited review is conducted either by the IRB Coordinator or a designated member of the IRB for certain categories. For more information about Limited Review, see step 5 below.
- Expedited review is conducted by a designated member of the IRB who may also be the IRB Coordinator.
- Full Board review is conducted by the convened IRB.
- Revisions step
Revisions are requested by the IRB Coordinator through the NuRamp system based on required elements of review and comments received from the designated Expedited reviewer or the IRB. All revisions are required to be completed via NuRamp within the specific form and are submitted by clicking on the “Submit Revisions” button via NuRamp.
Form statuses allow the IRB, the IRB Coordinator, and the research team to track a project and any subsequent form through their respective review timelines. There are a number of different statuses a project may have during the review process. A description of each status can be found on our Form Status sheet.
The quality, consistency, and complexity of the project information submitted may directly impact the number of revisions and overall length of review time.
Step 5: IRB Approval (Criteria, Review Level and Category)
Once the review process is complete, the IRB Coordinator will process approval via NuRamp and you will be notified via email. Be aware that ALL information from the IRB Coordinator is important and should be read carefully. Even though the IRB coordinators use similar language for each approval, they do include specific notes, points of clarifications, reminders or stipulations within the email notification and/or the official approval letters.
The IRB reviews all non-exempt research involving human subjects through an assessment of the following basic but required criteria, as it relates to the research, the review level and the proposed population per Policy #3.004, titled “Criteria for IRB Approval of Research.”
- Risks to subjects are minimized.
- Risks to subjects are reasonable in relation to the anticipated benefits to subjects and the advancement of knowledge.
- Selection of subjects is equitable in light of the research aims.
- Informed consent is sought from each prospective participant or legally authorized representative, and properly documented.
- The research plan makes adequate provision for monitoring the data collected to ensure safety of subjects.
- Adequate safeguards are in place to protect the privacy and confidentiality of subjects.
- Adequate provisions are made for the ongoing monitoring of the subjects’ welfare.
Three review levels with multiple categories allow the IRB to place projects in certain review levels.
It is important to note, the investigator will preliminarily select their review level or category upon new project form submission.
Upon submission, the IRB staff assign the Coordinator who then officially confirms the review level. It is not uncommon for the IRB Coordinator to change the review level based on the pre-review or consultation with HRPP staff, including the IRB Chairperson.
NOTE: The following descriptions have been truncated for ease of reference and quick comparison. Certain restrictions will likely apply to each category. For full category descriptions and limitations please review the Exempt and Expedited policies, 4.001 & 4.002, respectively.
Exempt (submission deadlines do not apply)
|
Exempt (submission deadlines do not apply) |
Exempt (submission deadlines do not apply) |
|||
| Category | Description | Category | Description | |
|
1 |
Research conducted in established or commonly accepted educational settings involving normal educational practices. |
1 |
Research conducted in established or commonly accepted educational settings involving normal educational practices. | |
|
2 |
Research involving the use of educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures, interview procedures or observation of public behavior to obtain non-sensitive data. NOTE: Certain exceptions apply to this category. Most notable, this category cannot include minors. |
2 |
Research that only includes interactions involving educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures, interview procedures, or observation of public behavior (including visual or auditory recording) if at least one of the following criteria is met:
a) no identifiers are collected NOTE: Certain exceptions apply to this category including the inclusion of minors. |
|
|
3 |
Research involving elected or appointed officials and all identifying information remains confidential for the life of the data. |
3 |
Research involving benign behavioral interventions in conjunction with other data collection from an adult only.
NOTE: Certain restrictions apply to this category including the inclusion of minors, interventions short in duration and authorized deception. |
|
|
4 |
Research involving the collection or study of EXISTING public and/or unidentifiable materials. |
4 |
Secondary research uses of identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens, if at least one of the following criteria are met:
a) The identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens are publicly available NOTE: There is no requirement that the information or biospecimens are pre-existing at the time of the IRB application; however, certain requirements in addition to IRB Exemption may be necessary such as a waiver of authorization if the data is regulated by HIPAA. |
|
|
5 |
Research involving the study of public benefit or service programs. |
5 |
Research involving the study of public benefit or service programs | |
|
6 |
Research involving a taste and/or food quality or consumer acceptance study. |
6 |
Research involving a taste and/or food quality or consumer acceptance study. | |
|
|
*7 |
Storage or maintenance for secondary research using identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens for which broad consent is required | ||
|
|
*8 |
Use of identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens for which broad consent is required for secondary research purposes |
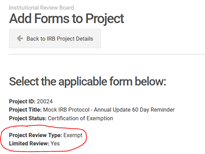
Certain Exempt categories when reviewed under the 2018 Requirements also require the IRB to conduct a Limited Review. Exempt with limited review is conducted by a designated member of the IRB for certain categories. The limited review process requires the review of certain criteria such as privacy and confidentiality as it applies to categories 2 and 3 above. Categories 7 and 8, above, require additional criteria as it applies to broad consent. All studies certified as exempt will have an official approval letter that will specify whether the project was reviewed as Exempt or as Exempt with Limited Review. Alternatively, you can view your project via NuRamp, click on the “Add a New Form” button, and verify whether your project was reviewed as Exempt or as Exempt with Limited Review via the page that appears.
*Exempt categories 7 & 8 would allow the storage, maintenance, and/or use of identifiable private information and/or biospecimens if broad consent was used. The current categories are included in the application to gauge the interest of the UNL research community in implementing the use of broad consent under the Exempt categories. At this time, it is the intention of the UNL IRB to potentially offer these Exemptions in the future as a way to reduce regulatory burden for investigators; however, there is also a considerable amount of work to be done to be able to ensure that the exemptions are implemented in a manner that meets all regulatory requirements, including the tracking of all non-consent for all projects using Exempt categories 7 & 8 at the institutional level. Although the UNL IRB will not be approving the use of broad consent at this time under the Exempt categories, all previous regulatory requirements through traditional informed consent for non-exempt (i.e., Expedited or Full Board) storage, maintenance, and research use involving identifiable information and biospecimens are still available.
Expedited (submission deadlines do not apply)
| Category | Description |
|
1 |
Certain clinical studies of drugs and/or medical devices. (very limited situations can this category be used) |
|
2 |
Collection of blood samples by finger stick, heel stick, ear stick, or venipuncture. |
|
3 |
Prospective collection of biological specimens for research purposes by noninvasive means. |
|
4 |
Collection of data through noninvasive procedures routinely employed in clinical practice, excluding procedures involving x-rays or microwaves. |
|
5 |
Research involving materials (data, documents, records, or specimens) that have been collected, or will be collected solely for non-research purposes (such as medical treatment or diagnosis). |
|
6 |
Collection of data from voice, video, digital or image recordings made for research purposes. |
|
7 |
Research on individual or group characteristics or behavior OR research employing survey, interview, oral history, focus group, program evaluation, human factors evaluation or quality assurance methodologies. |
Full Board (submission deadlines apply)
Full Board research generally involves that of greater than minimal risk, may include vulnerable populations and/or does not qualify for an Exempt or Expedited category. Additionally, a project can be reviewed at the Full Board level at the discretion of an IRB staff person.
Protocols reviewed at a Full Board meeting are assigned a lead reviewer based upon their expertise and they lead the IRB group discussion that covers the many criteria used to review projects (i.e. ensuring equitable subject selection, minimization of coercion, proportionate and reasonable risks and benefits, etc.) Quorum (more than half of the members present) is required to conduct most business at a convened Full Board meeting. If quorum is not met, the meeting will be adjourned and the project will be placed on the next month’s agenda.
NOTE: To be eligible for review, most Full Board projects must be submitted by the first business day of each month and is typically based on academic and/or holiday calendars. This is subject to change at the discretion of Research Compliance, Integrity, and Security. Full Board meeting dates and submission deadlines are posted on our website. Meetings are scheduled for the Spring, Summer, and Fall months based on IRB member schedules.
Step 6: Receive IRB Approval
After all requirements have been met or confirmed during the review process, the IRB could issue various forms of approval or a certification of exemption. Your approval will depend on the review level in which your project met the criteria discussed above.
- A project is “Approved by the IRB” if reviewed under the Expedited or Full Board categories.
- A project is provided a “Certification of Exemption” if the project is reviewed under the Exempt categories.
An IRB Coordinator will notify the Investigator(s) upon each form’s approval via email. The official IRB approval letter (with letterhead and regulatory references) is later available via NuRamp as a downloadable PDF.
Be sure to read both the unofficial and official email/letter very carefully as your coordinator may have provided you with suggestions, specifications, conditional approval stipulations, final notes, etc.
Step 7: Organize the research documents
After receiving approval, please be sure to take a moment and double-check that you understand how things are organized and available prior to starting your project. The following list of items are available via NuRamp:
- The “unofficial” email notification from your IRB Coordinator saying that your form has been approved. The official letter (with IRB letterhead) will come at a later time.
- The consent form/letter/script that includes the official IRB stamp, as applicable to your study.
- Exempt project documents will not be stamped.
- Non-exempt (e.g., Expedited or Full Board) project documents will always be stamped to ensure the IRB has a final record of which document contains the consent information. If this is not stamped or you cannot find it, please contact your IRB coordinator.
Additionally, investigators are encouraged to implement the use of version numbers to track the most up-to-date document. While there are many ways to approach version control of documents, this is the standard operating procedure used by Research Compliance, Integrity, and Security. Please feel free to reference and use this Document Version Control SOP as needed.
Step 8: Understand the responsibilities after approval
Protection of human subjects does not end with receiving IRB approval. After receiving approval and throughout the life of the project, there are several responsibilities that the Investigator(s) have in relation to the IRB. If things change within your project, they must be reported. If a situation arises that requires immediate notification to the IRB or you have “reportable new information,” it must be reported. If you are approved through an Expedited or Full Board method, the Investigator(s) must report annually to the IRB and must also report to the IRB when the project is completed. The following items will describe these requirements in more detail.
NuRamp will provide reminders for certain important dates investigators need to remember including:
- A reminder 30 days before your CITI training expires.
- A reminder at 60 days, 30 days, and 7 days prior to the lapse of an Expedited or Full Board project’s next update required date.
Modifications or Change Requests
Study materials may need to be revised or updated as a result of, for example, moving to remote activities, updating compensation terms, or changing inclusion/exclusion criteria. Overall, any study materials that the subject would see or hear would need to be updated. These would include any recruitment materials, template scripts, or letters that would be used to notify subjects regarding the change in study location and process, or consent forms that move from in-person signature to online e-signature procedures.
Review the UNL IRB templates webpage for any templates that could be used to make these changes including recruitment fliers and/or consent forms for social/behavioral research or e-consent.
- Exempt with Limited Review, Expedited, and Full Board: Any change in protocol must be reviewed and approved by the IRB prior to implementation except when an immediate change is necessary to eliminate a hazard to the participants as required under 45 CFR §46.108(a)(3)(iii).
- Exempt without Limited Review: Only the following changes must be submitted for review prior to implementation:
- A change in the scope of the project.
- A change that would increase risk to participants.
- A change that may alter the category of the original exemption determination.
- The project’s exemption falls under an exempt category requiring limited review.
- The addition or removal of a performance site.
- Change in Principal or Secondary Investigator.
- Addition of a new funding source.
- A change as directed by Research Compliance, Integrity, and Security.
Exempt projects only: All other changes not specified above and within a project that is active and has been Certified as Exempt do not require review and approval prior to implementation.
More information about changes and how they are reviewed can be found in Policy #12.001 titled, “Request for Change.”
Continuing Review
Continuing review forms are required to be submitted per the usual process under the Pre-2018 Requirements for all ongoing research and for all projects reviewed using the Full Board method of review.
A Continuing Review Form must be submitted prior to expiration of the approved project. All approved Pre-2018 Expedited and all Full Board projects regardless of Pre-2018 or 2018 Requirements will require a continuing review of research at intervals appropriate to the degree of risk, but no less than once per year as required under 45 CFR §46.109(e).
In order for a study to continue without interruption, the IRB must re-review and approve the protocol prior to the IRB approval expiration date. Continuing Review has to occur when:
- The research remains active for long-term follow-up of subjects, even when the research is permanently closed to the enrollment of new participants and all participants have completed all research-related interventions.
- The remaining activities are limited to collection and/or analysis of private identifiable information.
If an investigator does not provide continuing review information to the IRB, or the IRB has not approved the protocol by the expiration date, the investigator will be instructed to stop all research activities, including recruitment, enrollment, interventions, and interactions, and collection of private identifiable data, and to stop all interventions and interactions on current participants. However, exceptions are possible if the IRB finds an over-riding safety concern or ethical issue involved and it is in the best interests of individual participants to continue participating; however, this must be approved by the Board before this is allowed. New enrollment of participants is not allowed after the expiration of IRB approval.
More information about continuing review and how they are reviewed can be found in Policy #11.001 titled, “Continuing Review and Annual Update.”
Annual Update Form
An annual update form is required to be submitted for all Expedited projects that are not required to submit a continuing review form.
The annual update form provides the status of the project to the IRB and provides a few key reminders to Principal Investigators. The annual update form should be submitted prior to the requested date.
More information about the annual update form and how they are reviewed can be found in Human Research Protection Program Policy #11.001 titled, “Continuing Review and Annual Update.”
Final Reports
Final Report Forms are used to notify the IRB that the project has been completed. Final Reports are a requirement for all Expedited and Full Board approved projects ONLY.
More information about Final Reports Forms can be found in section 4.9 of Policy #11.001 titled, “Continuing Review and Annual Update.”
Reportable New Information
The Principal Investigator should report any adverse events or unanticipated problems within 48 hours of any of the research team members becoming aware of the incident. A comprehensive list of examples and definitions can be found in Policy #13.001 titled, “Unanticipated Problems Involving Risk and Adverse Events.” A Reportable New Information Form (RNIF) must be submitted to the IRB via NuRamp within 48 hours of the research team and ultimately the PI becoming aware of the situation.
For situations that arise in an active and approved project that must be reported to the IRB, please login to your specific project in NuRamp and click on “Add a New Form;” the RNIF is available as a form to be selected for completion. A detailed listing of what is required for reporting on the RNIF is also described in NuRamp where you select the form. If you have questions about the RNIF or a situation that may need to be reported, please do not hesitate to call or email your IRB Coordinator.
Protocol Deviations
Protocol deviations, per UNL HRPP policy #13.001, are defined as a departure from the approved protocol’s procedures made with or without prior IRB approval. Such departures may be major or minor/administrative in nature. A deviation is meant to be for one (1) individual or a very small group that accommodations are being made for and not necessarily changing your protocol for the entire study.
Minor or administrative deviations are those which do not “affect the scientific soundness of the research plan or the rights, safety, or welfare of human subjects.” Minor or administrative protocol deviations require reporting to the IRB at the time of continuing review/annual check-in for all non-exempt research and should be tracked using a protocol deviation tracking log (available on the UNL IRB templates webpage). Examples of minor or administrative deviations include the following:
- follow up visits occurring outside the protocol required time frame because of the participant’s schedule and does not affect the health or safety of the subject;
- biospecimen samples or study visits being completed/collected at times close to but not precisely at the time points specified in the protocol.
All major, non-emergent deviations are changes that the IRB must approve before the proposed change is implemented (via submission of a Reportable New Information Form). Examples of major, non-emergent deviations include the following:
- exceptions to eligibility criteria,
- exceptions to the form and manner of obtaining informed consent,
- and exceptions to the schedule of administration of an investigational product.






